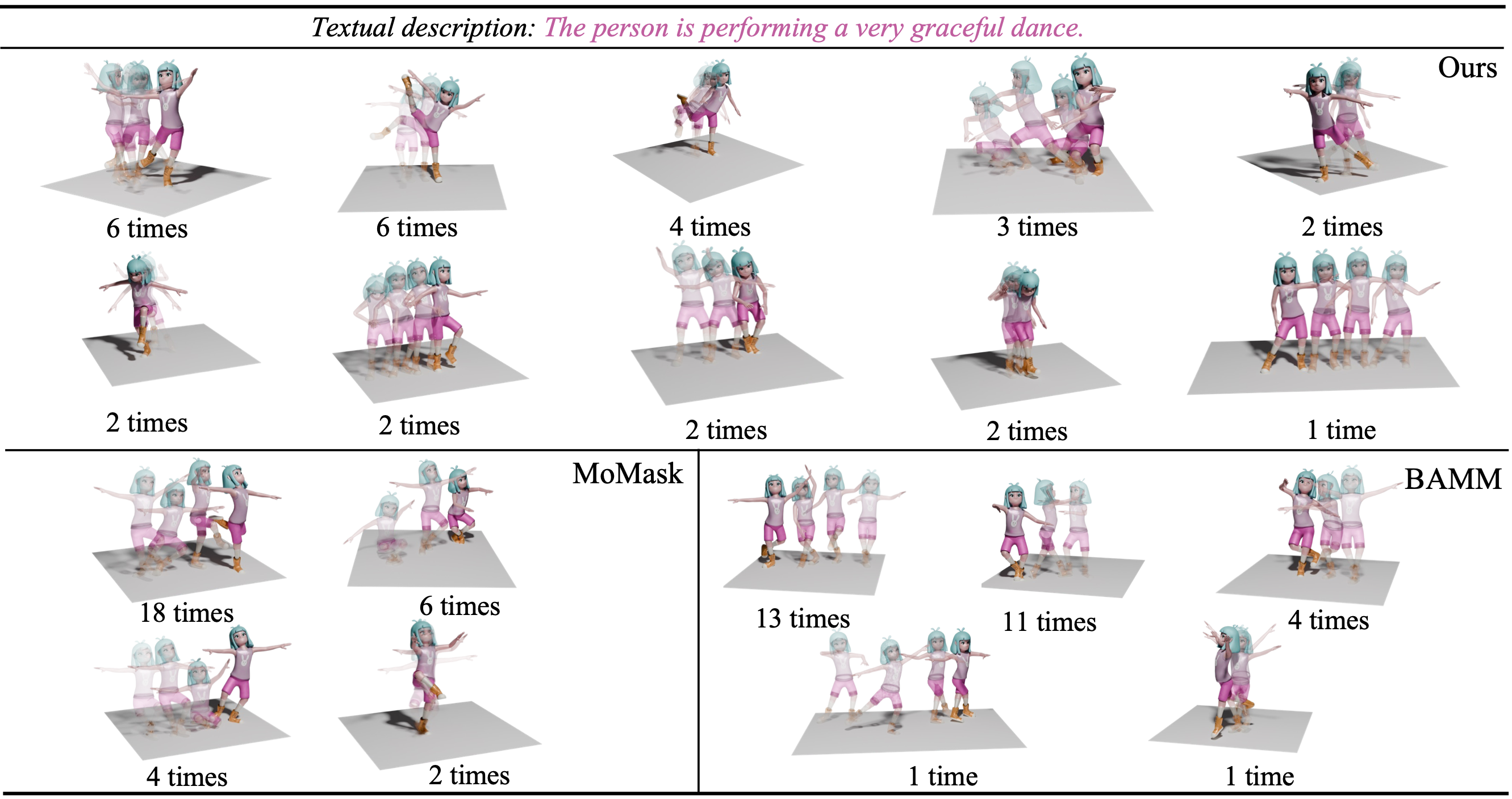
by MoMask
"a person is standing and adjusts their weight to lean more on their left side."
"a person slowly jogs to the right to left and the jogs back into place"
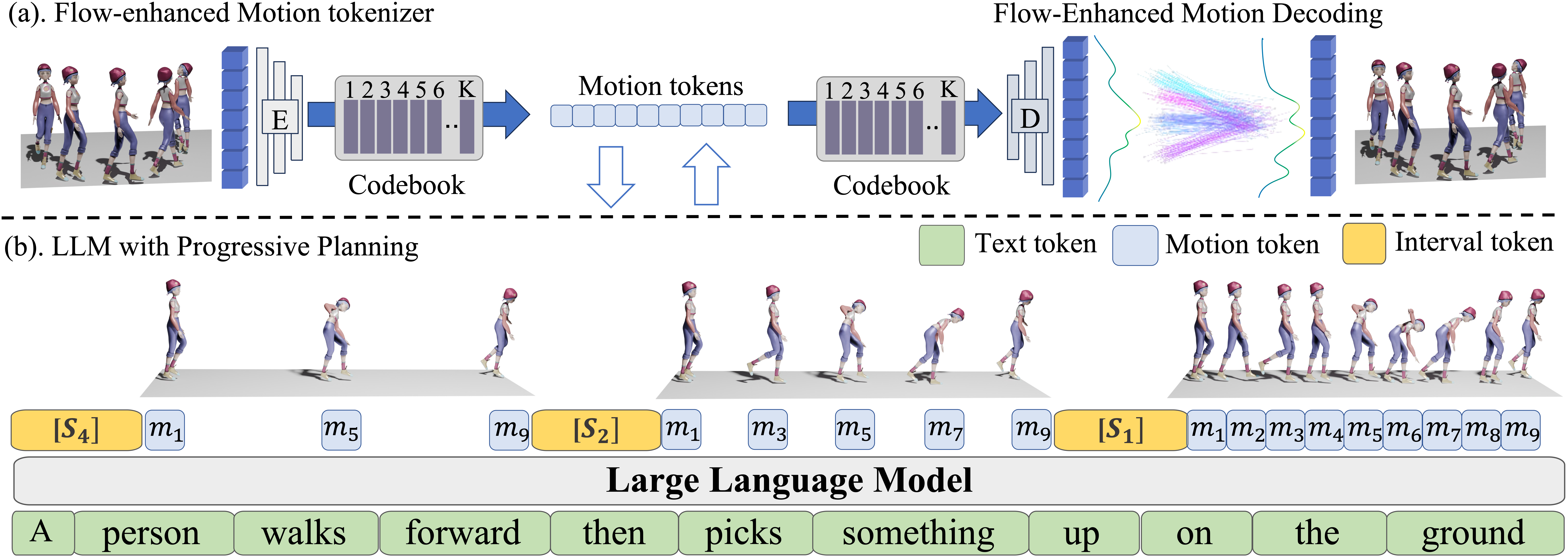
"The person begins by warming up their pectorals, waving their arms inwards and outwards. After completing this, they move their wrists in a circular motion in front of their face, simultaneously coordinating the movements with their ankles."
"The person walks around the floor, then runs forwards. After stopping, they stretch their elbows. Following this, the person, who is a man, raises his right hand over his head, then lets it back down next to his hip."
"The figure walks in a counterclockwise circle, stopping at their starting point. Then, they stand up from being on one knee. Finally, the person is looking at an accident."
"The sequence of motions is as follows: First, a person hops on their right foot. Then, a man walks slowly forward with his hands out to his sides, using an object on either side for balance. After that, the person walks in a curved path to the right. Finally, they slowly move their left hand from the right side of their body to the left."
"The person starts by walking in a circle. After completing the circle, they begin to walk forwards playfully, hopping slightly with each step. Midway through their playful walk, they respectfully take a knee for Black Lives Matter. As they rise from the kneeling position, they accidentally hurt their back."
"The person first bounces a ball to their right-hand side. Then, they swing a bat to their left twice. Following that, they wave widely with their right arm. Next, they dance side to side, moving their arms wide in and out. Finally, they grab something in front of them, swing it around to the side, and throw it overhead."
Text: The person walks around the floor, then runs forwards. After stopping, they stretch their elbows. Following this, the person, who is a man, raises his right hand over his head, then lets it back down next to his hip.
by PlanMoGPT
by MoMask
by T2M-GPT
Text: The figure walks in a counterclockwise circle, stopping at their starting point. Then, they stand up from being on one knee. Finally, the person is looking at an accident.
by PlanMoGPT
by MoMask
by T2M-GPT
Text: The sequence of motions is as follows: First, a person hops on their right foot. Then, a man walks slowly forward with his hands out to his sides, using an object on either side for balance. After that, the person walks in a curved path to the right. Finally, they slowly move their left hand from the right side of their body to the left.
by PlanMoGPT
by MoMask
by T2M-GPT
Text: The person starts by walking in a circle. After completing the circle, they begin to walk forwards playfully, hopping slightly with each step. Midway through their playful walk, they respectfully take a knee for Black Lives Matter. As they rise from the kneeling position, they accidentally hurt their back.
by PlanMoGPT
by MoMask
by T2M-GPT
Text: The person first bounces a ball to their right-hand side. Then, they swing a bat to their left twice. Following that, they wave widely with their right arm. Next, they dance side to side, moving their arms wide in and out. Finally, they grab something in front of them, swing it around to the side, and throw it overhead.
by PlanMoGPT
by MoMask
by T2M-GPT